Japan TELEC certification (Telecom Engineering Center Certification) is a mandatory certification system stipulated by Japan's Radio Law, executed by certification bodies authorized by the Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). All radio equipment sold or used in the Japanese market must pass this certification to ensure compliance with Japanese frequency regulations, radio frequency safety, and electromagnetic compatibility requirements.
With the implementation of multiple new regulations in 2025, the TELEC certification system has undergone significant changes. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the latest certification standards, item classifications, and compliance strategies.
TELEC certification, now officially named "MIC Certification," is Japan's sole radio equipment compliance assessment system, implemented according to the Radio Law and the Telecommunications Business Law.
Core Legal Requirements:
·Mandatory Certification: All devices emitting radio frequency signals (regardless of commercial use) require certification.
·Market Access Prerequisite: Products without the TELEC mark cannot pass Japanese customs and may face recalls, with manufacturers facing penalties.
·Regulatory Authority: The Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) is the regulatory body, and the Telecom Engineering Center (TELEC) is one of the primary certification bodies authorized by MIC.
Compared to PSE certification (for Electrical Appliance and Material Safety) and VCCI certification (voluntary electromagnetic compatibility certification), TELEC certification is a unique mandatory certification for radio equipment. In some cases, products may require mandatory PSE certification and/or JATE certification in addition to TELEC.
2. 2025 TELEC Certification Standard Update Highlights
Japan's radio equipment certification system underwent a series of important updates in 2025, with specific points as follows:
Technical Standard Updates (Effective Q4 2024)
·Wi-Fi 6E/7 Devices: Added ARIB STD-T109 v2.0 standard (for 6 GHz Wi-Fi 6E/7 devices).
·Bluetooth Devices: Require additional compliance with ARIB STD-T66 Amendment 3 (strengthened Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio ACLR requirements).
·UWB Devices: Must pass Pulse Template and Duty Cycle tests (referencing FCC Part 15 Subpart F).
Frequency Band Adjustments and Additions
·FM Broadcast Band Expansion: The upper limit of the FM broadcast band has been changed from 95MHz to 99MHz, affecting products like car radios and audio systems.
·New Band Opening: The 433.795MHz-434.045MHz band is allocated for Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) and Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) systems.
Device Testing Requirement Changes
·USB-C Interface Devices: Starting February 14, 2025, devices with USB-C interfaces require additional testing.
3. TELEC Certification Types and Item Breakdown
Starting in 2025, TELEC certification further refined the certification types, allowing companies to choose the appropriate certification path based on product characteristics and market strategy.
-Technical Compliance Certification
·Applicable Scope: Complete machines (e.g., mobile phones, routers).
·Characteristics: Comprehensive evaluation of the final product to ensure compliance with Japanese technical standards.
·Applicable Situations: Finished product equipment, small-batch products, customized equipment.
-Model Approval for RF Modules
·Applicable Scope: Independent RF modules (e.g., ESP32, nRF52840).
·Characteristics: Allows embedded reuse but requires a "Host-Module Consistency Declaration."
·Advantage: Module pre-certification can simplify the final product certification process.
Selection Strategy:
For products using standard RF modules, it is recommended to prioritize the Model Approval path, which can significantly reduce certification time and cost. For highly integrated custom devices, Technical Compliance Certification is more suitable.
4. TELEC Core Testing Standards and Technical Requirements
TELEC certification test items are quite comprehensive, mainly divided into the following categories:
Main RF Testing Standards
Different wireless technologies correspond to different testing standards. The following are the core testing requirements for main device types:
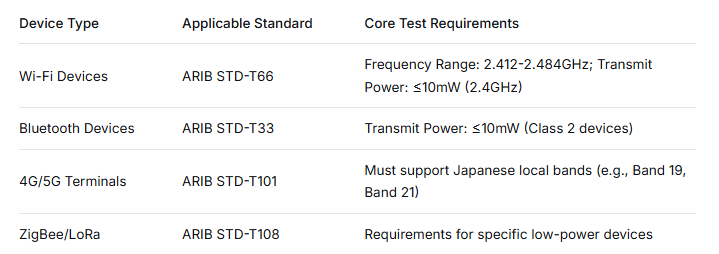
Other Test Items
·Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Testing: Ensures the device operates normally in the electromagnetic environment without causing harmful interference.
·Electrical Safety Testing: Some devices need to comply with Japan's Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (PSE certification) requirements.
Although the Japan TELEC certification process presents challenges, companies can complete the certification efficiently and compliantly by understanding the latest requirements, preparing in advance, and planning reasonably, thereby smoothly entering the Japanese market. BLUEASIA: +86 13534225140 will provide you with professional certification consulting services!
Japan TELEC certification, standards, ARIB STD, RF modules, technical compliance, model approval, 2025 updates
Related News