The core logic for wireless product market access in South Korea: Electronic devices with RF functionality must obtain both KC Safety Certification (including EMC/energy efficiency) and KCC RF Certification simultaneously. These two systems operate independently yet in tandem, and with the completion of KCC’s 2025 regulatory streamlining and standard upgrades, reliance on outdated certification experience will result in compliance failure. This guide provides actionable compliance solutions across four dimensions: system differentiation, core 2025 regulatory updates, dual certification pathways, and practical risk avoidance.
South Korea’s market access framework for electrical and electronic products features two core certification systems, and wireless RF devices require "dual certification." The governing bodies, core objectives, and requirements of these systems differ significantly—a critical prerequisite for avoiding compliance lapses:
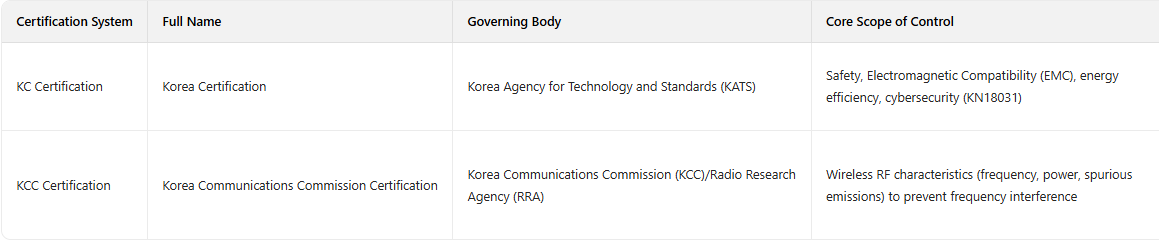
Critical Reminder: Starting in 2025, KCC RF certification test data must be synchronized to KC’s e-Certificate system. A data discrepancy exceeding 5% triggers manual review. A Shenzhen-based lighting manufacturer once experienced a 45-working-day certification delay due to this issue.
II. Core 2025 KCC Wireless RF Certification Updates (3 Key Changes: Streamlining and Tightening in Parallel)
In 2025, RRA’s adjustments to KCC certification focus on "regulatory streamlining" and "standard upgrades," with all core changes supported by official announcements and no subjectively imposed mandatory requirements:
1.Regulatory Optimization: Self-Compliance Verification Path for Low-Risk Devices
·Eligibility: Low-power devices with transmit power ≤10mW, such as BLE 5.3 and NFC products;
·Core Process: Instead of commissioning laboratory testing, enterprises only need to complete self-testing per KS X 3123:2025 and submit self-test reports plus compliance commitments to finish RRA filing;
·Benefits: Certification cycle reduced from the standard 4 weeks to 1–2 weeks, with testing costs cut by 60%. As of 2025, 30% of low-power devices have entered the market via this pathway.
2.Standard Upgrades: KS X 3123:2025 Revision and EMC Regulatory Synergy
·RF Standard Revision: KS X 3123:2025 adds testing guidelines for satellite mobile communication devices and simplifies RF stability testing procedures in industrial environments, reducing laboratory testing burdens by 25%;
·Mandatory EMC Synergy: Since January 2025, KCC RF certification must comply with the KN 32 EMC standard, with testing bands extended to 6GHz (5.925–6.425GHz). This band requires Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) to avoid radar signals within 200ms—a Dongguan-based router manufacturer saw a pass rate of less than 30% due to inadequate response speed;
·Frequency Band Adaptation: South Korea’s civilian 5GHz band is divided into three segments (5.15–5.35GHz, 5.46–5.72GHz, 5.725–5.825GHz) totaling 19 channels, with the 5.35–5.46GHz band (military-exclusive) prohibited for civilian use.
3.Forward-Looking Regulation: KS C3350 SAR New Standard to Take Effect in April 2026In July 2025, RRA issued Announcement No. 2025-44, specifying that starting April 1, 2026, all wireless devices in close contact with the human body must complete SAR testing per the KS C3350 standard:
·Core Change: Adoption of a unified East Asian human model (tailored to South Korean population body parameters) to replace the previously mixed European and American models;
·Transition Rule: Products launched before April 2026 may remain on the market, while new certified products after that date must meet the standard. Enterprises are advised to initiate testing by December 2025 to avoid laboratory backlogs during peak seasons.
III. Core Standards and Scope of KCC RF Certification (2025 Precision-Adapted Version)
1. Scope of Wireless RF Products Requiring Mandatory Certification
In 2025, KCC mandates RF certification for all products below (excluding exempted industrial-specific equipment):
·Consumer wireless terminals (Bluetooth speakers, smartwatches, WiFi routers);
·5G communication devices (Sub-6GHz modules, CPE terminals, limited to 3.5GHz/4.7GHz civilian bands);
·Satellite mobile communication devices (newly incorporated into the KS X 3123:2025 testing system);
·6GHz band devices (WiFi 6E/7 routers, requiring additional KN 32 EMC testing).
2. Core Testing Items (KS X 3123:2025 + KN 32 Synergy Requirements)
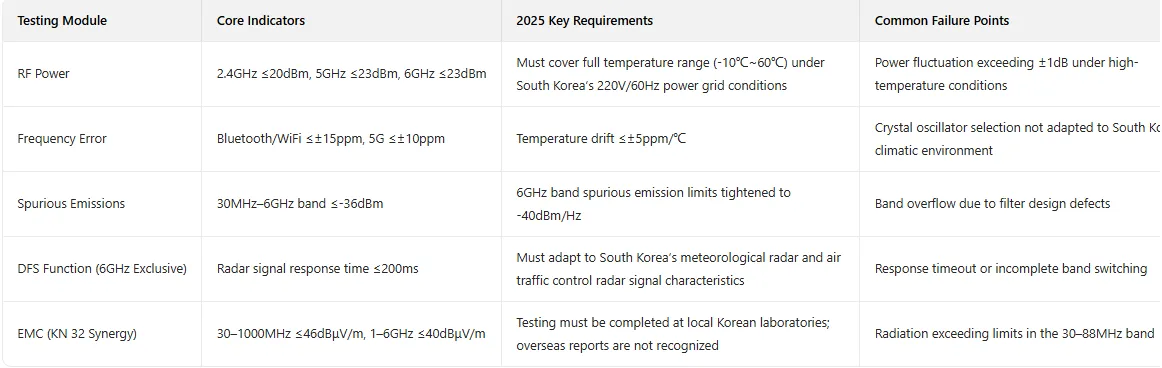
IV. 2025 Full Process of KCC+KC Dual Certification (Path-Specific Control to Avoid Cycle Traps)
Wireless devices must complete both certifications simultaneously. In 2025, KCC optimized process coordination, with overall timelines varying by product complexity: 4–8 weeks for standard products and 8–12 weeks for high-risk products (no fixed absolute timelines).
1. Low-Risk Devices (BLE/NFC): Self-Compliance + Basic KC Certification
·Enterprise Filing (≈1 week): Complete entity information registration in both RRA and KATS systems; non-Korean enterprises must appoint a local authorized representative;
·Self-Compliance Verification (1–2 weeks): Complete RF self-testing per KS X 3123:2025 and submit reports to RRA for filing;
·KC Safety Certification (2–3 weeks): Complete basic safety testing to obtain the KC mark;
·Data Synchronization (1 working day): Integrate RRA RF filing data into the KC certification number to complete market access.
2. Medium-to-High-Risk Devices (WiFi 6E/5G Modules): Laboratory Testing + Dual Certification
·Laboratory Selection (book 2 months in advance): Must select RRA-accredited local laboratories; EMC testing has been mandatory at local institutions since 2025;
·Joint Testing (2–4 weeks): Complete KS X 3123 RF testing and KN 32 EMC testing simultaneously; 5G devices require additional KN18031 cybersecurity testing under the KC system;
·Dual-System Review (2–3 weeks): Submit RF reports to RRA and safety/EMC reports to KATS; low-risk products qualify for AI-assisted review acceleration;
·Certificate Publication & Marking (1–2 weeks): Obtain a KC certification number (integrating RF compliance data); products must display the KC mark and the agent’s Korean address. In 2025, customs detained 83% of shipments with non-compliant marking.
V. Custom Dual Certification Pathways for 3 High-Frequency Product Categories
1. WiFi 6E Routers (6GHz Band)
·Core Requirements: KCC RF (6GHz DFS testing) + KC Certification (KN 32 EMC + energy efficiency);
·Key Challenge: Low pass rate for 6GHz band spurious emission and DFS testing. Using chips certified to KN 32 (e.g., MediaTek MT7922) can increase the pass rate to 91%;
·Cycle & Cost: Overall cycle of 6–8 weeks; 6GHz specialized testing accounts for 35% of total costs, with expedited services at local laboratories incurring a 50% premium.
2. Smartwatches (with Bluetooth/Heart Rate Monitoring)
·Core Requirements: KCC RF + KC Certification (safety + SAR);
·2025 Forward Preparation: Complete SAR testing with the East Asian human model per KS C3350 in advance to avoid post-April 2026 rectification;
·Compliance Warning: RF and SAR synergy data must be tested separately under charging conditions—a brand once faced a 2-week certification delay due to missing this test item.
3. 5G Industrial Modules (Sub-6GHz)
·Core Requirements: KCC RF (3.5/4.7GHz band adaptation) + KC Certification (industrial-grade anti-interference + KN18031 cybersecurity);
·Industry-Specific Requirement: Must provide RF stability reports under -40℃~85℃ conditions, which are subject to strict review by South Korean industrial clients;
·Optimization Tip: Prioritize KCC-certified modular chips to reduce certification costs by 40%.
VI. Post-Certification Compliance Maintenance
·KCC RF Certification: No fixed validity period; valid indefinitely if the product’s RF design remains unchanged and complies with current standards. Design changes require re-evaluation by RRA within 30 days;
·KC Safety Certification: Technical documentation must be retained for at least 5 years. High-risk products are subject to annual factory audits, with failure resulting in KC mark revocation.
If you are preparing for KCC mandatory certification for special products such as wireless terminals or 5G vehicle-mounted modules, you can share specific product functions, and we will provide customized dual certification pathways and testing checklists. BLUEASIA (+86 13534225140) offers professional certification consulting services.
Related News