For manufacturers targeting South Korea, KC (Korea Certification) is a mandatory legal hurdle for most electrical products. Administered by KATS (Korean Agency for Technology and Standards) under the Electrical Appliances Safety Control Act, its complexity and strict ongoing compliance are challenging. This article explains the KC certification landscape with 2025 updates.
KC is not one-size-fits-all. Requirements vary by product risk:
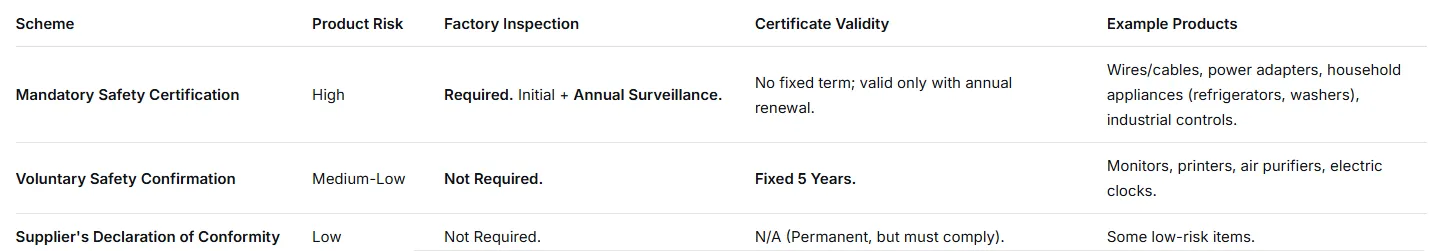
Determine your product's scheme first. Mandatory Safety Certification is the strictest path and the focus here.
II. KC Mandatory Certification Product Scope
Covers electrical products operating between 50V AC and 1000V AC, including:
-Wires/Cables, Switches, Capacitors/Filters
-Household Appliances (under 10kW): Refrigerators, washing machines, vacuums, irons.
-IT/Office Equipment: Monitors, printers, projectors, scanners.
-Audio/Video, Lighting, Power Tools.
-Power Adapters/Chargers, Transformers.
2025 Update: Some AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) devices have been newly added to the mandatory list.
III. Core KC Process & Documentation
A systematic process involving document review, sample testing, and factory inspection.
Preparation:
-Korean Authorized Representative: Non-Korean companies must appoint a local agent.
-Technical Documents: Korean manual, circuit diagrams, PCB layout, critical component list (KC or CB certificates for parts like PSUs/batteries), Korean label artwork with KC mark (height ≥5mm), certificate number, Korean product name, manufacturer & local agent info.
Testing:
-Safety Tests: According to Korean Standards (KN series).
-EMC Tests: Radiated/Conducted Disturbance.
-Samples: Typically 2-3 finished units.
-Optimization: Existing CB Test Certificates/Reports can exempt duplicate tests, saving time/cost.
Factory Inspection (Key for Mandatory Cert):
Initial audit followed by annual surveillance to maintain certificate validity. Focus: production consistency, quality management, control of critical components.
IV. KC Certificate Validity & Ongoing Compliance
A critical point: Mandatory KC certificates have no fixed expiry date. Validity depends on continuous compliance:
-Annual Factory Inspection: Required yearly (cost: several thousand RMB).
-Product Sampling: Market or factory audits by the certification body.
-Design Changes: Any modification affecting safety must be reported and may require re-testing. Unauthorized changes void the certificate.
Recommendation: Confirm your product's latest classification and standards via the KATS website or a reputable certification body before starting. Contact BLUEASIA: +86 13534225140.
相关新闻