In today's digital age, Canada's IC certification is a mandatory requirement for electrical and electronic equipment entering the Canadian market. Here is a clear, practical guide for efficient navigation.
IC Certification (Industry Canada Certification) is Canada's mandatory compliance scheme for electrical/electronic devices, enforced by Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED). It ensures products meet Canada's Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and radio communication regulations, preventing harmful interference to the radio spectrum.
Important Note: ISED was formerly Industry Canada, hence the "IC Certification" name.
IC certification is primarily split into two modes based on wireless functionality, with significant process/requirement differences:

2025 Key Policy Updates:
When planning and applying, pay special attention to these latest fee and regulation developments:
1.Fee Increase: Effective April 1, 2025, ISED implemented new fees. Official registration fee for a new IC-ID application is 804.14 CAD; modification fee is 402.07 CAD.
2.Clearer Labeling Specifications: New rules specify label format/presentation. Ensure the IC-ID format is correct and font height ≥1mm. For very small products, labels can be printed in the user manual if casing marking is impractical.
3.Certification Strategy Optimization: Enhanced alignment with U.S. FCC certification test reports allows for partial reuse, saving cost and time.
Certification Process & Key Steps:
The full IC certification process typically takes several weeks, depending on product complexity and path. Key stages:
1.Preparation & Product Classification (~1-2 weeks):
·Identify product category/applicable standards; prepare technical docs (schematics, manuals, etc.).
·For wireless products, provide a Canadian Local Representative's address and authorization letter.
2.Sample Testing (Core Phase):
Testing at an accredited lab. Main items:
·EMC Testing: Equipment's electromagnetic disturbance (conducted/radiated emissions) capability.
·RF Testing (IC-ID only): Frequency range, output power, bandwidth, spurious emissions, etc.
·SAR Testing (if applicable): Specific Absorption Rate testing for body-worn wireless devices (e.g., phones).
3.Report Review & Certification:
·IC-SDOC: Lab can issue conformity report directly (~1 week).
·IC-ID: Test reports submitted to a TCB (Telecommunication Certification Body) or ISED for review; certificate issued upon approval (~3-4 weeks).
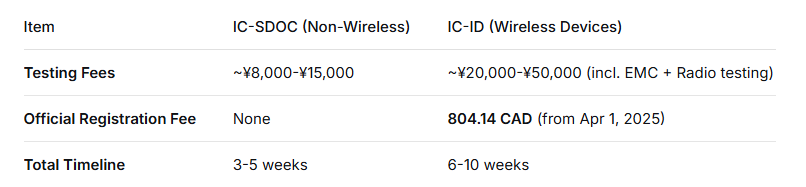
Costs & Timeline:
Costs primarily include testing, official registration, and agency service fees. Estimates by path:
We hope this guide provides a solid foundation. For detailed discussion on specific aspects of Canada's IC mandatory certification, feel free to consult BLUEASIA at +86 13534225140.
相关新闻