For electrical and electronic products planning to enter the Australian market, understanding the cost of SAA certification is a key step in budget planning. This certification is often the cornerstone of product safety compliance, with the RCM mark being the final market access pass.
To give you a quick overall idea of certification expenses, the table below summarizes the main cost components and reference ranges as of 2025.
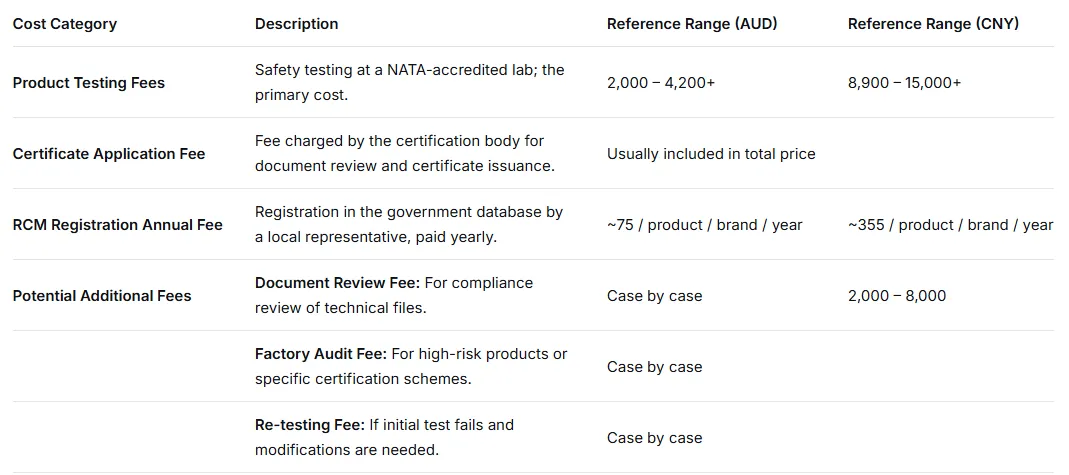
Key Factors Influencing Certification Cost:
Certification fees are not fixed and are mainly influenced by the following factors:
1.Product Risk Level & Complexity: This is the primary factor. High-risk products (e.g., heating appliances, medical devices) require more and stricter tests, typically costing about 30% more than ordinary products. The more complex the structure and features, the longer the testing takes, naturally increasing the cost.
2.Certification Scheme: There are two main paths.
·Type Test Approval: Primarily based on sample testing, relatively lower cost, but the certification body is only responsible for the tested sample.
·Full Certification Scheme: Involves factory inspection in addition to sample testing to verify production line quality control, thus higher cost, but with greater authority and broader applicability.
3.Possession of CB Report: If you already have a valid CB Test Report from the IECEE, you can apply for SAA certification through "conversion." This typically only requires supplementary testing for Australian/New Zealand national differences and is expected to save 30%-60% in testing costs compared to direct testing. It is the preferred path for cost and time control.
Practical Strategies to Optimize Certification Costs:
After understanding the cost structure, you can manage overall certification costs more effectively through several strategies:
1.Leverage CB Report Conversion: As mentioned, this is the most effective way to save. If your product targets global markets, consider applying for a CB Certificate early in the planning stage.
2.Bundle Applications for Similar Products: If you have a series of similar products requiring certification, consider submitting them for testing together. Experience shows that testing 5 models simultaneously could save up to 40% compared to individual testing.
3.Ensure Complete & Compliant Documentation: Ensuring technical files (e.g., circuit diagrams, manuals, critical component lists) are complete and compliant before submission can effectively avoid rework and additional review fees.
Australia SAA Certification Process & Important Reminders:
The typical SAA certification process involves engaging a certification body, sending samples for testing, preparing documents, review/certification issuance, and final RCM registration. The entire process usually takes 2 to 3 months.
When pursuing certification, please pay special attention to the following:
·Mandatory Requirements: SAA certification is mandatory for products listed on the Declared Electrical Articles list (can be checked in standard AS/NZS 4417.2). Selling products without certification or proper RCM marking risks prohibition of sale, forced removal from shelves, and significant fines.
·Local Representative Requirement: Overseas manufacturers applying for SAA certification and RCM registration must appoint an Australian local importer or authorized agent as their legal representative.
·Certificate Validity & Maintenance: The SAA Certificate of Suitability has a maximum validity of 5 years. During its validity, companies must ensure mass production is identical to the certified sample and may require annual surveillance audits (for products requiring factory inspection) to maintain certificate validity.
We hope this detailed cost breakdown for Australian SAA Safety Certification helps you better plan the certification budget for exporting products to Australia. If you can share more specific product categories (e.g., small appliance, lighting, IT equipment), BLUEASIA: +86 13534225140, will provide you with professional certification consulting services!
相关新闻