Background to the Launch of China's Robotics CR Certification:
In 2015, the National Development and Reform Commission issued a project plan for industrial transformation and upgrading (enhancing the core competitiveness of manufacturing), identifying robotics as a key product for development within the intelligent manufacturing sector.
China has become the world's largest robotics market. It is projected that by 2020, the annual production of domestically branded industrial robots in China will reach 100,000 units, while the annual sales revenue of service robots is expected to exceed 30 billion yuan.
To regulate the rapidly expanding robotics market, the NDRC, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ), Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), and Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA) formally launched the ‘China Robot Certification (CR)’ mark in November 2016, marking the substantive commencement of standardised testing and certification for robots.
The CR certification mark carries three meanings:
1) Robot Certification;
2) China Robot Certification;
3) China Robot.
The CR emblem's overall design evolves from the letter R nested within the letter C, presenting a dynamic robotic figure set against a full circle. The circular emblem symbolises protection, infinity, and wholeness. The agile robot moving freely within the circle represents the robotics industry, shielded by certification, brimming with boundless energy and momentum. It signifies the sector's vigorous development and a harmonious future.
The CR mark employs orange, a colour widely used in safety signage for its seriousness and professional connotations. This underscores the certification's influence and authority.
The CR mark is the unified certification emblem for robotic products. When applied, the certification body's name is combined with the basic emblem to reflect its primary certification responsibility. Supplementary letters denote certification types: S for safety certification; E for electromagnetic compatibility certification; E and S together signify combined safety and electromagnetic compatibility certification.
Testing Scope for Different Robot Categories:
Industrial Robots:
Performance testing, safety assessment, and evaluation of intelligence levels and reliability for various industrial robots, AGVs, specialised robots, and intelligent manufacturing systems;
Factory calibration, online calibration, non-standard testing, fault diagnosis, and quality enhancement services for industrial robot products;
Installation positioning for industrial robots and high-end equipment, post-maintenance inspection and evaluation services;
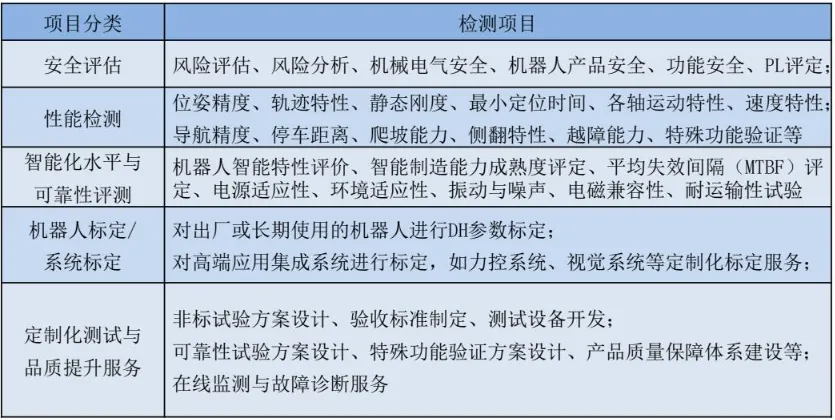
Primary testing items for industrial robots:
Service Robots:
Systematic and objective testing, certification, non-standard testing, fault diagnosis, and bespoke consultancy services for household and commercial service robots, drones, mobile robots, educational/entertainment robots, cleaning robots, medical robots, etc., covering safety, functional performance, voice interaction, and intelligent attributes.
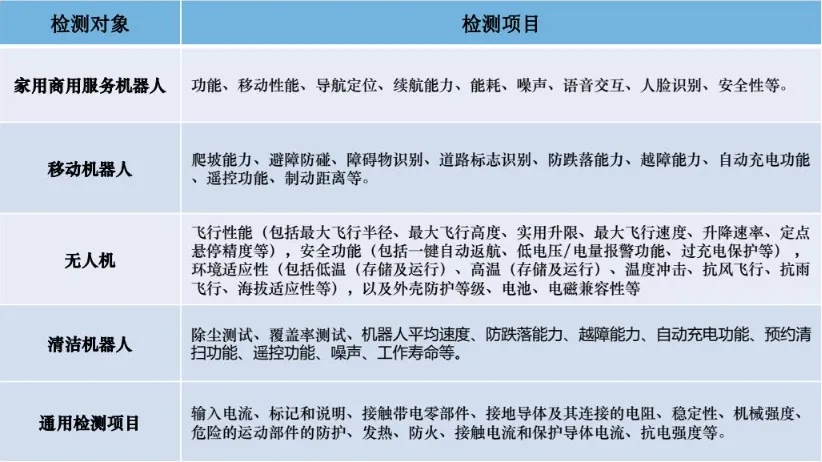
Primary testing items for service robots:
Domestic and Commercial Service Robots:
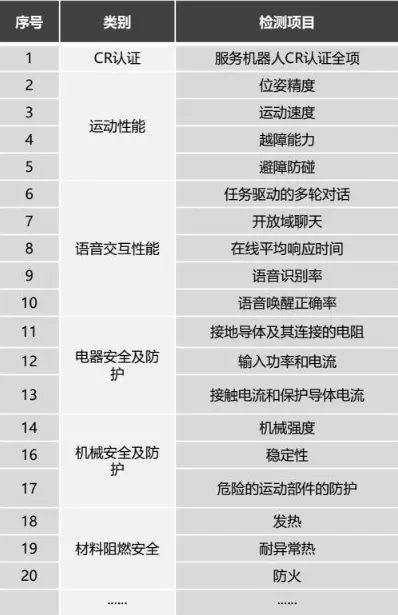
Testing categories encompass motion performance, voice interaction capabilities, electrical safety protection, mechanical safety safeguards, and material flame retardancy.
Voice interaction performance testing includes: task-driven multi-round dialogue, open-domain conversation, online average response time, speech recognition accuracy, and voice wake-up accuracy.
Key Testing Items for Domestic and Commercial Service Robots:
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs):
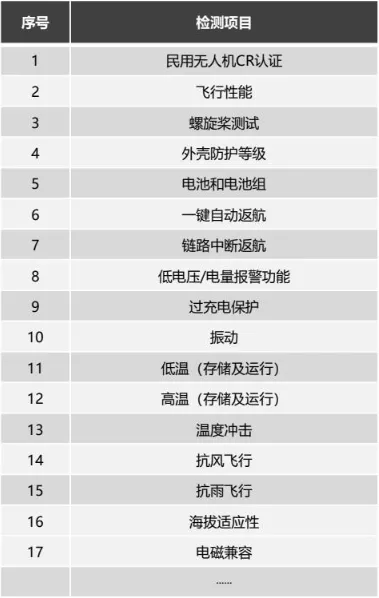
Tests evaluate flight performance, overall system safety, and reliability of airborne equipment.
Flight performance metrics include: flight attitude stability, maximum flight radius, maximum flight altitude, service ceiling, maximum flight speed, climb/descent rates, electronic fencing, resume-flight accuracy, navigation precision, heading accuracy, remote control range, stationary hovering accuracy, flight accuracy, and flight trajectory.
Primary inspection items for drones:
Cleaning Robots:
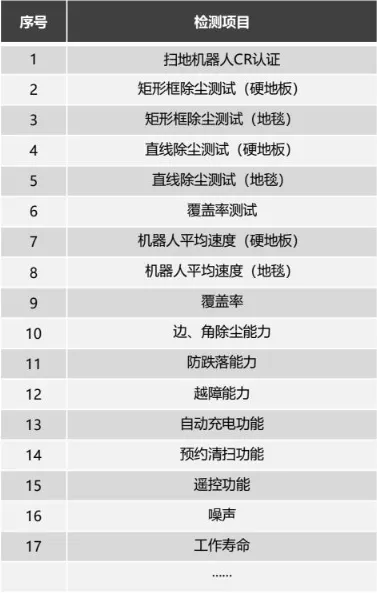
Key testing items: dust removal efficacy, coverage rate, average robot speed, fall prevention capability, obstacle clearance capability,
automatic charging functionality, scheduled cleaning capability, remote control functionality, noise levels, operational lifespan, etc.
Additionally, products may undergo testing for electrical safety, mechanical safety, material flame retardancy, environmental adaptability, electromagnetic compatibility, and other relevant parameters.
Key Testing Items for Cleaning Robots:
Value of CR Certification:
Robotics certification advances national adoption and international mutual recognition. Certification objectives include but are not limited to:
1. Enhancing policy support precision and product market credibility through certification adoption;
2. Securing national and regional financial subsidies and policy backing for the robotics industry;
3. Providing value assessment for corporate financing and technological mergers within the robotics sector;
4. Demonstrating robot product quality to users through internationally recognised professional test reports;
5. Providing technical verification of key robotics technology maturity through alignment with international standards;
6. Promoting the transformation and upgrading of China's manufacturing sector while enhancing corporate core competitiveness.
Certification Modes
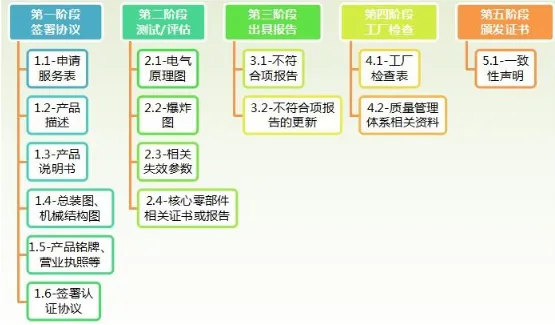
CR Certification Process:
Includes: Industrial Robot CR Certification, Service Robot CR Certification, UAV CR Certification
1. Application
• Selection of certification mode
• Certification unit division
• Submission of certification documentation
2. Inspection Phase
• Type testing: Typically 30 working days
• Initial factory inspection: 2–4 working days
3. Evaluation and Approval
• Certificate issued within 30 working days of passing
4. Post-Certification Management (Mode B)
• Post-certification surveillance
• Re-evaluation
• Certification certificate
• Use of certification mark
Blue Asia Technology possesses globally recognised testing capabilities for wireless products, offering BQB, SRRC, CR certification (robotics), FCC, IC, CE, CarPlay, Android Auto, RCM, MIC, R&D and connectivity software testing, alongside multi-country certification transfer services for Southeast Asia, the Middle East, South America, and Africa.
Should you require further information or testing services, please contact us by telephone. We shall provide the optimal solution tailored to your specific product requirements.
Consultation Contact: Benson
Mobile: (+86) 13632500972
Email: marketing@cblueasia.com
Address: Building C, Hongjingda Industrial Park, No. 107 Beihuan Road, Shiyan Subdistrict, Bao'an District, ** City
| |||||||||
优势项目 | |||||||||
无线充Qi | 蓝牙BQB | 苹果MFi | USB-PD快充 | 中国SRRC | |||||
认证项目 | |||||||||
大中华China | 质检报告 | CCC | CQC | CTA | SRRC | BSMI | NCC | OFCA | |
亚洲Asia | METI | TELEC | PSE | JATE | VCCI | KC | BLS | SASO|IECEE | |
欧洲EU | CE | RoHS | REACH | EN71 | PAHS | GS | WEEE | ERP | |
美国Americas | FCC | IC | Rro65 | CEC | DOE | ETL\UL | CSA | NOM | |
其他Othericas | CB | UN38.3 | IEC62133 | EN50332 | RCM | MEPS | SAA | ||
汽车电子Auto-Eiectronic | E-mark | MFi | Carplay | CarLife | Android Auto | ||||
测试项目 | |||||
汽车|军工电子EMC | 消费电子EMC | Radio | Safety | 语音质量测试 | 语音识别测试 |
验货与验厂 | |||||
验货 | 验厂 | 社会责任审核 | 质量管理体系 | BSCI | SEDEX |