This article consolidates publicly available information for general guidance. IMDA policies and fees are subject to change. Always refer to the official IMDA website (https://www.imda.gov.sg) as the definitive source before making business decisions.
Singapore's IMDA certification is a mandatory requirement for telecommunications and wireless devices entering the Singapore market. To assist with clear and efficient budget planning, below is a detailed breakdown of 2025 certification costs, influencing factors, and practical cost-optimization strategies.
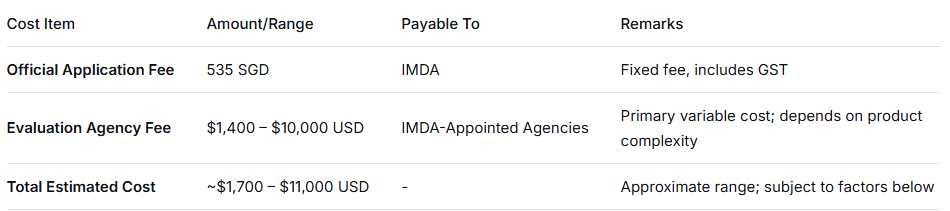
Total IMDA certification fees consist of a fixed application fee and variable evaluation fees. The table below outlines key cost components:
Additional Fee Notes:
·Application Fee: Some certification modes may waive this fee. For example, IMDA has previously exempted ESER registration fees for SMEs.
·Evaluation Fee: Paid to IMDA-recognized third-party evaluation bodies. Cost varies significantly based on product complexity and testing scope (e.g., simple Bluetooth headset vs. multi-mode 5G phone).
Key Cost Factors:
Understanding these factors helps estimate final certification expenses:
1.Certification Mode Selection: This is the primary factor determining cost and timeline. IMDA uses three main modes based on device type and risk level:
·ESER (Enhanced Simplified Equipment Registration): For low-power short-range devices like Bluetooth/Wi-Fi. Based on **Supplier's Declaration of Conformity (SDoC); fastest process, may have waived fees.
·SER (Simplified Equipment Registration): For cellular devices like mobile phones.
·GER (General Equipment Registration): For base stations and other high-risk or non-listed devices. Most stringent requirements, often requiring certification by an IMDA-recognized body, thus typically the most expensive.
2.Technical Complexity & Test Scope: More complex product features require more testing, increasing costs. For example, devices supporting multiple frequency bands and complex modulation schemes incur significantly higher RF and EMC testing costs than simpler products.
3.Leveraging Existing Reports: Internationally recognized test reports (e.g., FCC, CE) might be accepted by IMDA, avoiding duplicate testing and saving associated costs.
IMDA Certification Process & Timeline:
Besides cost, understanding the process and timeline is crucial. The core IMDA certification process is:
1.Document Preparation: Compile technical files, test reports, etc.
2.Application Submission: Submit via IMDA's TERS system.
3.Fee Payment: Pay application and evaluation fees.
4.Review & Testing: IMDA and evaluation bodies review documents, conduct supplementary tests if needed.
5.Certificate Issuance: IMDA issues the certificate upon approval. Valid for 5 years.
Timeline varies by mode: ESER: ~1-2 weeks; SER & GER: ~4-6 weeks.
Important Notes:
·Local Representative Requirement: Applications must be submitted by a Singapore-registered company holding a valid Telecommunications Dealer's License.
·Certificate Validity: IMDA certificates are typically valid for 5 years. Plan for renewal before expiry.
·Labeling Requirement: Certified devices must be permanently marked: "Complies with IMDA Standards [XXXXXX-XX]", where the number is the local representative's business license number.
We hope this detailed breakdown of IMDA certification costs aids your budget planning. For a more targeted certification pathway analysis based on your specific product (e.g., Bluetooth device, phone, base station), contact BLUEASIA at +86 13534225140 for professional certification advisory services.
相关新闻