A complete CE-EMC certification is far more than a one-time test. It's a systematic compliance verification from product design to market launch, where process smoothness, timeline controllability, and agility in responding to regulatory changes collectively determine a product's successful entry into the EU.
Understanding CE-EMC requires a 3D view: the X-axis is the standardized process, the Y-axis is the flexible timeline, and the intersecting Z-axis represents the ever-changing regulatory and product risk variables.
All three are intertwined. Process complexity dictates timeline length, while product type and latest regulations (e.g., 2025's mandatory cybersecurity rules) are the core variables affecting both. For instance, an ordinary LED lamp and a smart gateway with integrated Wi-Fi/Bluetooth follow vastly different certification paths, timelines, and scrutiny depths.
The legal cornerstone is the EU EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), aiming to ensure equipment functions correctly in its electromagnetic environment without causing unacceptable interference to other devices.
II. Process Deconstruction: Four Key Stages
Stage 1: Preparation (1-2 weeks) – The efficiency & cost foundation.
-Determine Directives & Standards: Identify applicable EU directives. Almost all electrical products need EMC. Mains-powered? Add Low Voltage Directive (LVD). Wireless? Add Radio Equipment Directive (RED). Then, pinpoint specific harmonized standards (e.g., EN 55032 for multimedia, EN 55014 series for appliances).
-Prepare Samples & Technical Data: Provide 2-3 final production intent samples. Start compiling key files: circuit diagrams, EN user manual, BOM.
Stage 2: Testing Execution (Core timeline variable)– Samples go to an accredited lab.
-EMI (Interference) Tests: Ensure "doesn't interfere" – e.g., Conducted & Radiated Emissions.
-EMS (Immunity) Tests: Ensure "isn't susceptible" – e.g., ESD, Radiated Susceptibility, EFT/B, Surge.
-For Wireless Products: Must add RED RF performance tests (e.g., EN 300 328). Critically, from August 1, 2025, wireless products must also undergo mandatory cybersecurity assessment per EN 18031 series.
Stage 3: Technical File & Declaration of Conformity
Post-testing, the manufacturer compiles the complete Technical File (product description, design drawings, test reports, risk assessment, user manual). Finally, the manufacturer/EU Rep signs the legal **EU Declaration of Conformity (DoC).
Stage 4: Filing & Marking
The Technical File must be kept within the EU for at least 10 years for surveillance checks. After all steps, the CE mark can be affixed—clear, indelible, minimum 5mm height.
III. Timeline Details: From Weeks to Months of Variability
There's no fixed answer. The timeline stretches like a rubber band, mainly pulled by product complexity and test results.
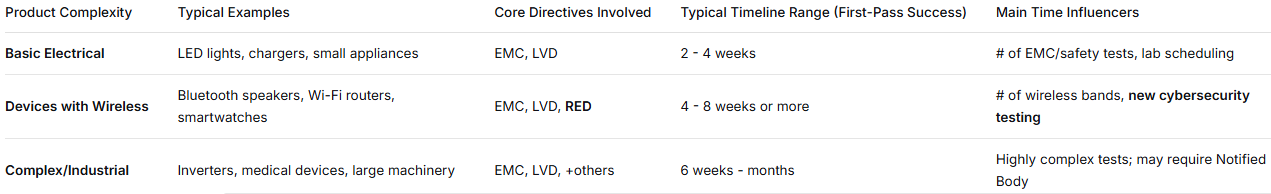
The biggest "time killer" is test failure and rectification. This can easily add 1-3 weeks or more for design mods, new samples, and retesting. Using a lab offering pre-compliance testing or design-phase consulting mitigates this risk. Lab backlog (busy season delays) and a company's own document prep efficiency also impact total duration.
IV. 2025 New Rule Variables Affecting Process & Timeline
Two major 2025 updates introduce key variables, primarily affecting wireless devices** and potentially extending timelines.
Variable 1: Cybersecurity Mandatory for Wireless Devices
Per EC Decision (EU) 2025/138, EN 18031 is now a RED harmonized standard. From Aug 1, 2025, certification for wireless devices (smart home, wearables) must add a cybersecurity assessment to existing RF & EMC tests. This may involve code review, vulnerability scans, encryption checks, adding complexity and time.
Variable 2: Core Harmonized Standard Version Updates
The May 2025 (EU) 2025/893 decision set clear expiry dates for old versions of key standards. For example, new versions for EN 301 489 series (EMC) and EN 301 893 (5GHz Wi-Fi) are published, with old versions phasing out before end-2026. Manufacturers must ensure testing against the latest effective standard version. Confirming this at project kick-off avoids costly rework.
V. Process Optimization: How to Make Certification Smoother & More Controllable?
1.Implement "Front-Loaded" Strategy: Involve certification consultants or review designs against target standards during the R&D phase, reducing design-defect-led rectifications at the source.
2.Utilize "Pre-compliance Testing": Conduct key item tests on engineering samples before formal submission. This "dress rehearsal" finds and fixes most EMC issues early at lower cost, greatly boosting first-pass rate and controlling total timeline/cost.
3.Systematic Document Management: Create standardized Technical File templates and update circuit diagrams/BOMs during routine R&D. Complete, accurate files speed up agency review.
4.Choose Partners Wisely: Select accredited bodies that also offer regulatory interpretation, standard update alerts, and localized support. Their understanding of new rules (e.g., 2025 cybersecurity) saves you trial-and-error time.
A Zhejiang garden tool maker learned this the hard way. Their new Bluetooth chainsaw's certification was halted mid-process due to unaddressed RED and cybersecurity rules. After redesign and reassessment, the timeline ballooned from 8 to 24 weeks, missing the Black Friday sales season entirely. The workshop chief lamented, "We thought it was just an extra certificate; turns out we had to re-engineer the product."
In 2025, with technical standards and geopolitics intertwined, compliance is no longer just a technical hurdle but a cornerstone of trust in international commerce.
BLUEASIA Tech: +86 13534225140 provides professional certification consulting services.
Related News